The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has committed to enable ‘Insurance for All’ by 2047, where every citizen has appropriate life, health and property insurance cover and every enterprise is supported by appropriate insurance solutions and also to make the Indian insurance sector globally attractive. In FY23, total premium of the Insurance Industry grew at a healthy 16% to Rs. 2.56 Lakh Cr. As per the IRDAI, India will be the sixth-largest insurance market within a decade, leapfrogging Germany, Canada, Italy, and South Korea.
In this Blog, we shall get an understanding of the General Insurance Industry in India:
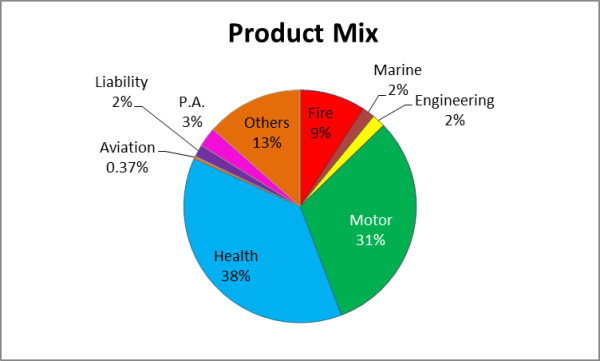
Mainly, there are 2 types of insurance, General and Life insurance. General insurance consists of Health Insurance, Motor Insurance, Fire Insurance, Property Insurance & Crop Insurance. Let’s dive deeper into each of these segments:
Health Insurance
The country’s health insurance sector is at an inflection point on account of a convergence of various factors. More than 1/3rd of the General Insurance market in India is dominated by health insurance. The incidence of unexpected medical challenges (pandemic, for instance) and related costs has created a dire need for protection. Medical costs in organised health care facilities are perpetually rising, infuenced by the introduction of advanced medical treatment. According to data by online insurance broker PolicyBazaar, the average ticket size of retail health insurance in India has increased to Rs 26,533 so far in FY24, up 48% from Rs 17,900 in FY19. According to a recent report by insurtech Plum, India’s medical inflation has reached 14 percent, posing a financial strain on individuals who bear their own healthcare expenses.
There is a growing recognition that India can grow equitably if the benefits of health insurance are extended wider across rural India (where insurance coverage penetration is considerably lower than the Indian urban average). There is a higher product innovation done by focused players to cater to the individual needs of customers.
To boost the health insurance sector IRDAI came up with the licensing of SAHI (Standalone Health Insurance Companies) under which 6 health insurance-focused companies operate in India. This segment is dominated by Star Health & Insurance.
Motor Insurance
Third-party motor insurance is a vehicle insurance policy that is mandatory for vehicles like trucks, cars, jeeps, bikes, scooters, etc. This policy offers coverage to the vehicle owner against legal damages to be paid to compensate for losses by the third parties that are involved in such accidents. Demand in this segment is driven by Sales of new automotive vehicles as well as renewal of expiring policies. The newly launched vehicle scrappage policy should be a further trigger for growth in this segment.
The yearly premiums that you pay for the motor insurance policy are meager as compared to the advantages and protection the coverage will offer you in case of mishaps. Though there are many misconceptions regarding the policy, it will most certainly compensate you against the physical damage that arises under different circumstances.
Fire insurance
It is a specialized form of insurance designed to provide financial protection against losses caused by fire, lightning, explosion, and implosion. This type of insurance holds importance for both individuals and businesses. For individuals, it ensures the safety of their homes and personal belongings, while for businesses; it safeguards assets and operations, preventing severe disruptions.
Other Insurance segments include Crop, Marine & Aviation Insurance.
What makes the general insurance business so attractive?
General insurance is a business in which the policyholders pay premiums upfront and make claims later. This creates a negative working capital and allows the insurers to invest this money and earn investment income during this period. This is called float. A well-managed general insurer consistently raises float and earns investment income on it for long periods. This makes general insurance an attractive business to own, provided the cost of the float, which is the underwriting loss, is less than the return on the float.
Insurance Industry terminologies:
Gross written premium (GWP) = Total premium underwritten by an insurer, before other expenses.
Claim ratio = Net claims settled/ net premium collected. Gives the ratio of claims which were paid vs. premiums collected.
Loss ratio = (Claim related losses/total premiums earned). Percentage that compares the amount of claims paid vs. the total amount of premium the company earned.
Combined ratio = (Claim related losses + operating expenses)/ total premiums earned). Used to measure the overall profitability of the insurer.
Accounting for Insurance companies is significantly different than for other companies. Insurers have to provide for claim reserves (Provision for future payments for claims) for long-term motor TP policies on an undiscounted basis which results in a higher claims ratio and thus higher underwriting losses at the start. Also, deferment of acquisition costs is not allowed in India and all expenses flow through the income statement as they happen. This means that even though the policy may be for 3 years, expenses made for an acquisition of the same shall hit the Profit & Loss account fully in the first year itself. This means that even though the policy may be for 3 years, expenses made for an acquisition of the same shall hit the Profit & Loss account fully in the first year itself. However, this is going to change going forward after the applicability of IFRS 17 (IND AS 117) as against the erstwhile IFRS 4 which MCA is yet to notify.
How to identify good quality insurers?
- Cost of funds: Calculated as underwriting profit or loss divided by float. There are some companies that have an underwriting profit, thus implying that they are being paid for earning the float
- Return on the float: investment income/ float. Rates of return are largely constant across the general industry as most of the investments are in fixed-income securities.
- Leverage: Float divided by the net worth. Similar to banks, good quality insurers having higher leverage gives rise to higher Return on Equity. Leverage is a factor of the product mix as in businesses like third-party motor insurance claims are settled over a long period of time which allows the insurer to retain float for a longer period of time.
High-quality general insurers differentiate themselves on their ability to raise the low cost of liabilities i.e. by sound underwriting practices. If companies are able to raise float at low cost it is consistently able to earn a high ROE.
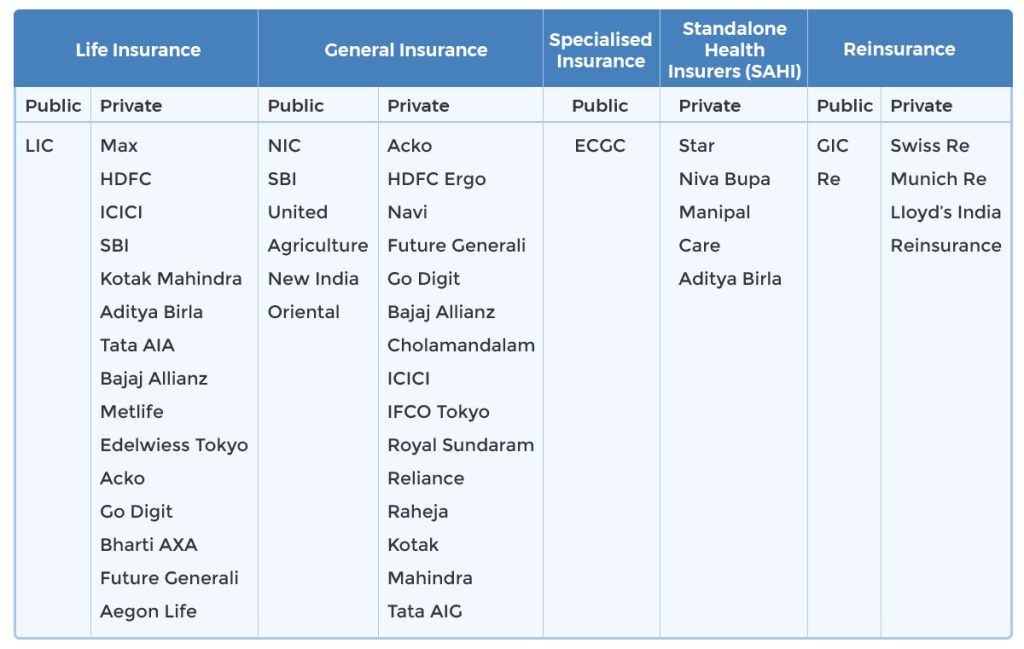
Segment-wise Industry Participants
Growth drivers
- Medical inflation and increased awareness about insurance, particularly health among people.
- The emergence of new distribution channels, like online selling of policies, allows insurers to have a pan-India reach
- Increasing disposable income among people
- Increased regulatory support. E.g. Bima Sugam
- Insurers can now launch new health products without the prior permission of IRDAI
Recent Developments: Bima Sugam
The IRDAI on March 19 gave the go-ahead to launch an online marketplace for insurance called ‘Bima Sugam’. It is a part of IRDAI’s Bima Trinity - Bima Vistaar, Bima Vahak, and Bima Sugam.
Bima Sugam is an online platform where customers can choose a suitable scheme from multiple options given by various companies. All insurance requirements, including those for life, health, and general insurance (including motor and travel) will be met by Bima Sugam. The hallmark of this platform is its streamlined, paperless claim settlement process, leveraging policy numbers for both health coverage and death claims. According to industry leaders, Bima Sugam could reduce the dependence of insurance companies on intermediaries and promote the sale of products through direct digital means. IRDAI described Bima Sugam as a ‘UPI-like moment in insurance’ – a one-stop solution for all stakeholders including - customers, insurers, intermediaries, and agents to promote transparency and efficiency and boost insurance penetration in the country to achieve the vision of “Insurance for all by 2047”.
...Already have an account? Log in
Want complete access
to this story?
Register Now For Free!
Also get more expert insights, QVPT ratings of 3500+ stocks, Stocks
Screener and much more on Registering.






 Download APP
Download APP




















Comment Your Thoughts: