OLA Electric Mobility Limited IPO Details:
IPO Date: August 2, 2024 to August 6, 2024
Total Issue Size: ~80.86 Cr shares
Fresh Issue: ~ 72.36 Cr shares
Offer for Sale: ~ 8.49 Cr shares
Price band: Rs. 72 – Rs. 76 per share
IPO Issue Size: ~ Rs. ~6,145.56 Cr
Lot Size: 195 shares and multiples thereof
About OLA Electric Mobility Ltd:
OLA Electric is an integrated pure EV (Electric Vehicles) manufacturing player in India and currently builds 2-wheeler EVs and EV components. They manufacture EVs and core EV components such as battery packs, motors and vehicle frames at their factory in Tamil Nadu. They have launched 4 products and have announced 6 new products since their first product announcement in August 2021. Ola Electric has cornered roughly ~35% share in the electric 2-wheeler market by volumes in India in FY24.
Ola Electric has R&D centres in India, UK and the United States which focus on designing and developing new EV products, core EV components and are in the process of building an EV hub in Tamil Nadu, which includes their Futurefactory, their upcoming Gigafactory and co-located suppliers.
Ola also operates its own direct-to-customer (D2C) Omni channel distribution network which comprises of 935 showrooms and 414 service centres situated across India. Ola’s network of showrooms was India’s largest company-owned network of experience centres as of 2023.
Industry Overview:
The Indian automotive market produced 2.6 crore vehicles in FY23 (excluding electric rickshaws). The industry contributes approximately 35% to manufacturing GDP and 5-6% to overall GDP. India is a global hub for two-wheeler (2W) production, producing nearly 2 crore 2Ws, making it the second-largest 2W producer globally, with around 40 lakh units exported each year. The domestic 2W market size is valued at Rs. 1.4-1.6 trillion. Scooters, popular for their ease of use and utility, dominate the 2W segment. Affordable price segments (less than Rs. 1 lakh ex-showroom) constitute 86% of scooter and 77% of motorcycle sales, driven by price-conscious middle class consumers.
Despite higher prices which are limiting 2W penetration to 160 per 1000 people, there is significant growth potential, primarily on account of increasing disposable income of the Indian consumers. The 2W sales volume, currently below pre-pandemic levels, is expected to grow at an 11% CAGR over the next five years, reaching a market size of Rs. 2.8 trillion by FY28. This growth is expected to be fuelled by the growing middle class, urbanization, and supportive policies.
All vehicle segments are moving towards electrification, with shared mobility (3-wheelers, commercial vehicles, taxis) adopting EVs faster because of better total cost of operation (TCO). E-commerce intermediaries, logistics companies, and government fleets are also transitioning to EVs, due to ambitious green emissions targets laid out by the government as well as themselves. In personal mobility, 2Ws are leading the shift due to lower cost differences between electric and ICE vehicles, making them more affordable for Indian consumers. Electric 2Ws have a 45% lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) compared to ICE vehicles, breaking even in about two years due to relatively stable electricity costs versus rising fuel prices. However, it is worth noting that this statistic ignores the cost of battery replacement, which is estimated to be ~87 thousand for the Ola S1 Pro which is 60% of the scooter’s on-road price. This remains a key impediment in calculating the TCO benefits.
Electric 2W penetration has increased significantly in India, reaching ~4.5% of 2W registrations in FY23 and ~5.1% in H1 FY24. This reduced slightly in Q2 FY24 due to reduced FAME subsidies.
(Ola launched its products in Dec 2022)
Key governmental initiatives enabling electric 2-wheeler adoption in India:
- National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020 was launched in 2013. This plan also includes the FAME subsidy introduced by the central government
- Production-linked Incentive Scheme for Auto sector and cell chemistry
- State subsidies on EVs
- Charging Infra co-development initiatives
Ola Electric’s History:
Ola Electric had acquired Netherlands-based electric 2W manufacturer Etergo in the year 2020 and the Ola S1 series of scooters is based on the concept of App Scooter made by Etergo.
Manufacturing setup:
Ola Electric manufactures its electric 2W and other components at its factory called as the Ola “Futurefactory”. Ola claims to have set up the Futurefactory in eight months with an installed capacity of 10 lakh units per year as of October 2023.
Ola is also setting up the Ola Gigafactory, where it plans to manufacture battery cells at a large scale in this factory. The construction of this factory commenced in June 2023 and is located in close proximity to the Futurefactory. Ola had planned to complete the first phase of Gigafactory by March 2024 with a production capacity of 1.5GWh and plans to expand it to 6.4GWh from the proceeds of the issue. Although, news reports state that the plant has become operational with a capacity of 5GWh. This factory has a potential production capacity of 100 GWh of cells.
Ola Gigafactory
Ola Model Basket:

(There is negligible road tax levied on EVs)
The company follows a direct-to-customer strategy for retailing its products. According to Ola Electric, following this model helps it directly engage with its customers and collect feedback accordingly.
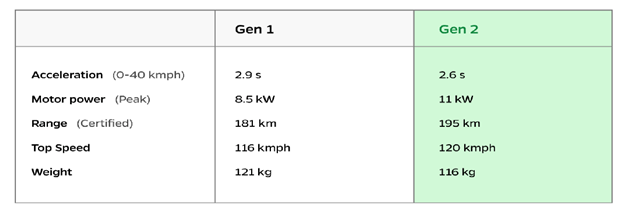
Ola Electric had delivered its first product, the S1 Pro in December 2021, followed by the S1 in September 2022. The company has launched its S1 Air and S1X range in 2024. In August 2023, the company revamped its line-up by introducing the 2nd generation of its model line-up. This revamp brought better efficiencies to its products-such as lighter weight, better battery management and increased range. The 2nd generation serves as the base for its entire scooter line-up, existing as well as new.
Comparison of Gen 1 and Gen 2 S1 Pro
Ola Electric has also announced a range of motorcycles, which it estimates to begin delivery by H1FY26.
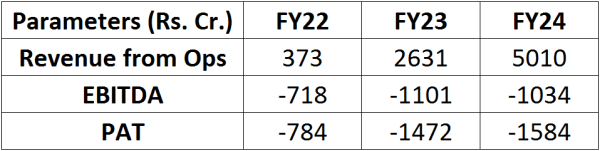
Financials Snapshot:
Even though the company is scaling up its revenue at a significant pace, Profits are a distant dream at present with the company incurring a loss of Rs. 1584 Cr in FY24. The path to profitability for the company remains to be an event to watch out for.
Purpose of Issue:
The company plans to go for an IPO primarily for:
- Capex expenditure by subsidiary OCT (Ola Cell Technologies) to expand the capacity of a cell manufacturing plant to 6.4 GWh.
- Repayment of debt incurred by subsidiary OET (Ola Electric Technologies)
- Investment in R&D
- Expenses for additional experience centres
- General corporate purposes
- Give initial investors such as Matrix an exit, which may be partial or complete.
Competitive Landscape:
Ola Electric’s competitors are mainly Ather Energy, TVS with its iCube range and Bajaj with its Chetak. There are other players as well which mainly import Chinese electric CKD (completely knocked down) kits and assemble them in India.
Positives:
- Ola is steadily increasing its production as well as going for a massive, large scale production, which will boost economies of scale which will help achieve better unit economics.
- End to end integration-from development to sales which helps lower costs.
- Ola plans to foray into additional segments like motorbikes which will further boost growth.
Challenges:
- Ola is loss-making since its inception and losses are increasing year on year.
- Product Quality: Customers have reported multiple defects in the quality of products, some of which require complete replacement of battery packs and other components.
- Service Quality: The Company’s after-sales service leave a lot to be desired. This is due to the fact that the service centres are currently understaffed.
- Dependence on FAME Subsidy: The Company is dependent on subsidies by the centre as well as by individual states to make their products competitive and at an affordable price point. Any reduction or withdrawal of these subsidies will deliver a serious hit to EV Players such as OLA.
Management:
Bhavish Aggarwal: He is the founder, Chairman and Managing director of Ola Electric. He has also founded ANI Technologies (Ola Cabs) in 2010. He completed his BTech in computer science and engineering from IIT Bombay.
Harish Abhichandani: He is the Chief Financial Officer of the company. Prior to joining Ola Electric, he was associated with ANI Technologies as CFO, Tata Communications as vice president and Tata Waterhouse Securities as CFO.
MoneyWorks4Me Opinion
Ola Electric operates in a highly competitive industry with products which are not exceptional in the true sense. The overall competitive edge of traditional players remains strong because of distribution and service reach, this combined with reducing FAME subsidy and unfavourable total cost of ownership (after including battery replacement costs) poses a significant challenge to Ola Electric. Ola is looking to gain early mover advantage in lithium-ion cell manufacturing, however these projects are exposed to execution and technology obsolescence risks and thus would need to be monitored. The issue commanding a market cap of Rs. 33,500 Cr seems to be aggressively priced based on the post issue price to sales multiple in excess of 6.5 times with profitability being some years away.
We recommend investors to AVOID subscribing to Ola Electric.
OLA Electric Mobility Limited IPO Tentative Timetable:
| IPO Activity | Date |
| IPO Open Date | August 02, 2024 |
| IPO Close Date | August 06, 2024 |
| Basis of Allotment Date | August 07, 2024 |
| Refunds Initiation | August 08, 2024 |
| A credit of Shares to Demat Account | August 08, 2024 |
| IPO Listing Date | August 09, 2024 |
Retail Individual Investor IPO Lot Size:
| Application | Lots | Shares | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 1 | 195 | Rs. 14,820 |
| Maximum | 13 | 2535 | Rs. 192,660 |
OLA Electric Mobility Limited IPO FAQs:
When will the OLA Electric Mobility Ltd IPO open?
OLA Electric Mobility Ltd IPO will open for subscription on Friday, 2nd August 2024, and closes on Tuesday, 6th August 2024.
What is the price band of OLA Electric Mobility Ltd IPO?
The price band for OLA Electric Mobility Ltd IPO is Rs. 72-76/share.
What is the lot size for the OLA Electric Mobility Ltd IPO?
Retail investors can subscribe to the IPO minimum lot size is 195 shares, up to a maximum of 13 lots i.e. Rs. 1,92,660/-.
What is the issue size of OLA Electric Mobility Ltd IPO?
The total issue size is ~ Rs. 6,145.56 Cr.
When will the basis of allotment be out?
Allotment will be finalized on August 7th and refunds will be initiated by August 8th. Shares allotment will be credited in Demat accounts by August 8th.
What is the listing date of OLA Electric Mobility Ltd’s IPO?
The tentative listing date of the OLA Electric Mobility Ltd IPO is August 9th, 2024.
What if I do not get the allotment?
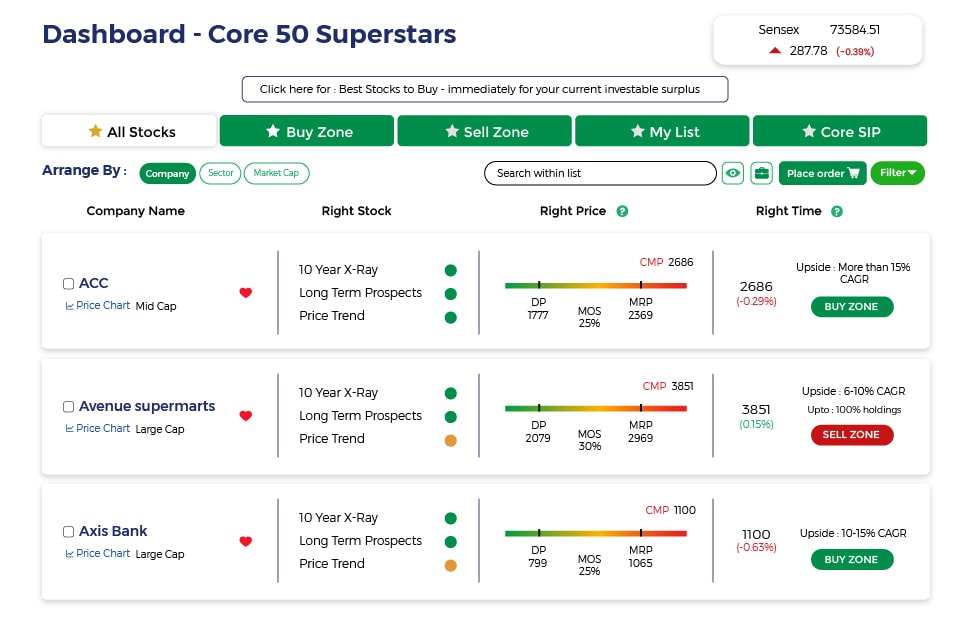
If you do not get an allotment of this IPO we recommend you to check out our MoneyWorks4me Core Superstars which helps you build a strong portfolio right away. It offers a Model Portfolio of high-quality stocks Buy/Sell alerts on Quality stocks at a reasonable price and SIP recommendations on stocks. With the help of MoneyWorks4me Core Superstars, you would have picked winners like Asian Paints, Divis Labs, Titan, Pidilite, Cipla, Bharti Airtel, and ICICI Bank.
Already have an account? Log in
Want complete access
to this story?
Register Now For Free!
Also get more expert insights, QVPT ratings of 3500+ stocks, Stocks
Screener and much more on Registering.












 Download APP
Download APP



















Comment Your Thoughts: