1. Introduction
The Indian Four-Wheeler (4W) sector is a significant contributor to the nation's automotive industry, economy, and employment. It encompasses a wide range of passenger vehicles, including hatchbacks, sedans, SUVs, and luxury cars, catering to diverse consumer needs and preferences. This comprehensive deep-dive analysis aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the Indian four-wheeler sector, covering historical development, market dynamics, key players, market share dynamics, challenges, opportunities, and future prospects.
2. Historical Perspective
The history of the Indian 4W sector dates back to the early 20th century when a few international automakers started assembling cars in the country. However, it wasn't until the post-liberalization era in the 1990s that the sector witnessed significant growth and transformation. Key milestones include:
- Pre-Independence Era: Limited presence of automobiles, primarily luxury cars for the aristocracy.
- Post-Independence to 1980s: Restricted import policies resulted in the emergence of Hindustan Motors (Ambassador) and Premier (Padmini) as early Indian car manufacturers.
- 1990s: Liberalization led to the entry of global players such as Maruti Suzuki, Tata Motors, and Hyundai.
- 2000s: Rapid expansion and modernization, introduction of new models, and improved safety and emission standards.
- 2010s: The emergence of SUVs, electric vehicles (EVs), and increasing focus on safety and emission norms.
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Size and Growth
The Indian 4W market has experienced significant growth over the years, driven by factors such as rising disposable incomes, urbanization, improved road infrastructure, and increased consumer aspiration. The market size has consistently expanded, with annual sales reaching millions of units.
3.2 Market Segmentation
The Indian 4W market is segmented into several categories, including:
- Hatchbacks: Compact and affordable vehicles, often favored by urban commuters.
- Sedans: Mid-size and full-size cars catering to families and corporate consumers.
- SUVs: Sports Utility Vehicles, including compact, mid-size, and luxury SUVs, which have gained popularity due to their versatility and road presence.
- Luxury Cars: High-end vehicles from premium brands, attracting affluent buyers.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs are gaining traction due to environmental concerns and government incentives.
3.3 Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumer preferences in the Indian 4W sector are evolving:
- Safety: Consumers prioritize safety features like airbags, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and electronic stability control (ESC).
- Fuel Efficiency: Fuel-efficient models, including hybrid and electric cars, are becoming more popular.
- Connectivity: Infotainment systems, smartphone integration, and connectivity features are increasingly important.
- Sustainability: Growing environmental awareness has led to interest in EVs and cleaner technologies.
3.4 Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape in India's 4W sector includes several key aspects:
- Bharat Stage (BS) Emission Standards: These standards govern vehicle emissions, with stricter norms introduced periodically to reduce pollution.
- Safety Regulations: India is gradually adopting global safety standards, making features like airbags and ABS mandatory.
- Taxation and Incentives: Government policies impact vehicle prices, with EVs often benefiting from incentives to promote adoption.
- Import-Export Policies: Trade agreements and tariffs affect the import and export of 4W vehicles and components.
4. Key Players
4.1. Tata Motors
Tata Motors is one of India's oldest and largest automotive manufacturers, offering a diverse range of 4W vehicles under the Tata brand. It has a significant market presence with models like Tata Tiago, Tata Nexon, and Tata Harrier. Tata Motors has also ventured into electric vehicles, including the Tata Tigor EV and Tata Nexon EV.
4.2. Maruti Suzuki India Limited
Maruti Suzuki is a dominant player in the Indian 4W market, known for its affordability and extensive distribution network. Models like the Maruti Suzuki Alto, Maruti Suzuki Swift, and Maruti Suzuki Dzire have consistently topped the sales charts. The company is actively exploring the EV segment.
4.3. Mahindra & Mahindra
Mahindra & Mahindra (M&M) is a major player in the SUV and UV (Utility Vehicle) segment. Models like Mahindra Scorpio, Mahindra Bolero, and Mahindra XUV500 cater to both urban and rural consumers. M&M is also involved in electric mobility, with offerings like the Mahindra eKUV100 and Mahindra eVerito.
4.4. Hyundai Motor India Limited
Hyundai is a global automaker with a significant presence in India. Models like Hyundai Creta, Hyundai Venue, and Hyundai i20 are popular choices among Indian consumers. The company is actively exploring alternative fuels and electric mobility.
4.5. Toyota Kirloskar Motor
Toyota is known for its reliability and quality. Models like Toyota Innova Crysta and Toyota Fortuner have a strong presence in India. Toyota is also investing in hybrid technology and exploring EVs in the Indian market.
5. Market Share Dynamics
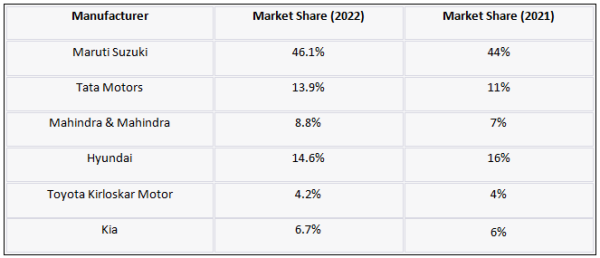
5.1. Market Share by Manufacturer
The market share of 4W manufacturers in India is dynamic and can fluctuate annually. Below is a table illustrating the market share of key manufacturers in the recent past:
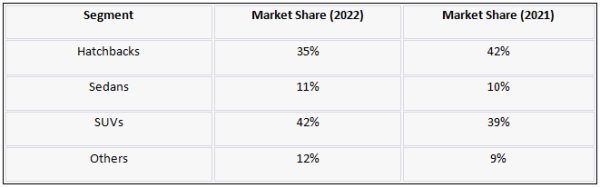
5.2. Market Share by Segment
The market share within various 4W segments can provide insights into consumer preferences. Below is a table illustrating the segment-wise market share:
5.3. Market Share by Fuel Type
The market share of different fuel types, including petrol, diesel, and electric, is an important indicator of changing consumer preferences. Below is a table illustrating the market share by fuel type:
6. Challenges and Opportunities
6.1. Challenges
The Indian 4W sector faces several challenges:
- Environmental Concerns: Meeting stringent emission norms while maintaining fuel efficiency is a continuous challenge.
- Safety Compliance: Adhering to evolving safety standards can increase manufacturing costs.
- Market Saturation: In urban areas, the market may become saturated, requiring companies to focus on rural expansion.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Events like the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted supply chain vulnerabilities.
6.2. Opportunities
The sector also presents numerous opportunities:
- Electric Mobility: The adoption of electric vehicles presents growth potential.
- Technological Advancements: Embracing advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and connected vehicles.
- Export Markets: Exploring international markets for exports.
- Customization: Offering customized options to cater to diverse consumer preferences.

7. Future Prospects
The Indian 4W sector's future is promising:
- Electric Revolution: EV adoption is expected to grow, driven by government incentives and environmental concerns.
- Connected Mobility: Smart vehicles with advanced connectivity features will gain traction.
- Shared Mobility: Shared mobility services like ride-sharing and car subscriptions will evolve.
- Safety and Autonomous Driving: Increased focus on safety and gradual movement toward autonomous vehicles.
The Indian 4W sector continues to be a cornerstone of the nation's automotive industry and economic growth. As the sector adapts to changing consumer preferences, stringent regulations, and environmental concerns, it must innovate and invest in technology to thrive. With a growing focus on electric and connected mobility, the future of the Indian 4W sector holds exciting opportunities for both manufacturers and consumers.
...Already have an account? Log in
Want complete access
to this story?
Register Now For Free!
Also get more expert insights, QVPT ratings of 3500+ stocks, Stocks
Screener and much more on Registering.

































Comment Your Thoughts: